To play around with Node.js streams, I made a simple ‘toy’ version of jq, a handy command line JSON processor.
To be clear, the real jq utility is very lightweight and has a ton of functionality. In this post I’ll be mimicking some of it’s functionality and using Node.js to do so.
This will of course result in a bloated tool with way more bundled in than what we actually need.
That being said, it’ll be a useful exercise to go through to learn a little bit about Node.js streams.
In the github repository, you’ll see how easy it is to hack together a very simple command-line tool to process data streamed in from stdin.
Node.js Streams
The stream documentation describes them as as:
A stream is an abstract interface for working with streaming data in Node.js. The
streammodule provides an API for implementing the stream interface.
For this example I’ll be jumping straight into the Transform Stream – stream.Transform. This is a duplex stream, where the input would usually be related to the output in some way.
Transforming Input from stdin
The basic use of a Transform stream in Node.js (to process input from stdin) looks like this:
const {Transform} = require('stream')
const TransformStream = new Transform;
TransformStream._transform = (chunk, encoding, callback) => {
// do something with the chunk
console.log(chunk.toString().toUpperCase());
callback();
}
process.stdin.pipe(TransformStream);
Toy jq Utility With Transform Streams
I created a ‘toy’ version of jq using a Node.js Transform stream. It’s a very quickly hacked together example, so don’t expect it to do everything that jq can do. I’m also fully aware that the real jq utility is a very lightweight tool and that doing this in the Node.js runtime adds a lot of unecessary bloat!
This is purely for demonstration purposes.
Packaging up the Node.js app with pkg, we get a platform specific binary called toyjq.
Examples
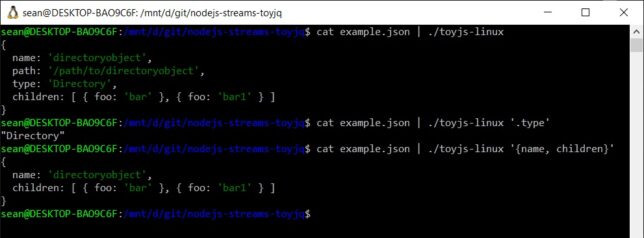
Pretty print input JSON
cat ./example.json | toyjq-linux
{
name: 'directoryobject',
path: '/path/to/directoryobject',
type: 'Directory',
children: [ { foo: 'bar' }, { foo: 'bar1' } ]
}
Output the `type` field only from input JSON:
cat ./example.json | toyjq-linux
cat ./example.json | toyjq-linux '.type' "Directory"
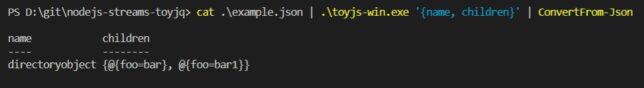
Output just the `name` and `children` fields in the input JSON:
cat ./example.json | toyjq-linux '{name, children}'
{
name: 'directoryobject',
children: [ { foo: 'bar' }, { foo: 'bar1' } ]
}
Assuming now the Windows platform version of toyjq, and using a PowerShell cmdlet for this example…
Select the children array, convert it to an object in PowerShell and then select the last item in that object array:
(cat .\example.json | .\toyjq-win.exe '.children' | ConvertFrom-Json).foo | Select -Last 1 bar1
The above examples show how you can easily process data from one input pipeline (stdin in this case) and send it along through the pipeline using Node.js streams.
You can find the example toyjq app on my GitHub repository.