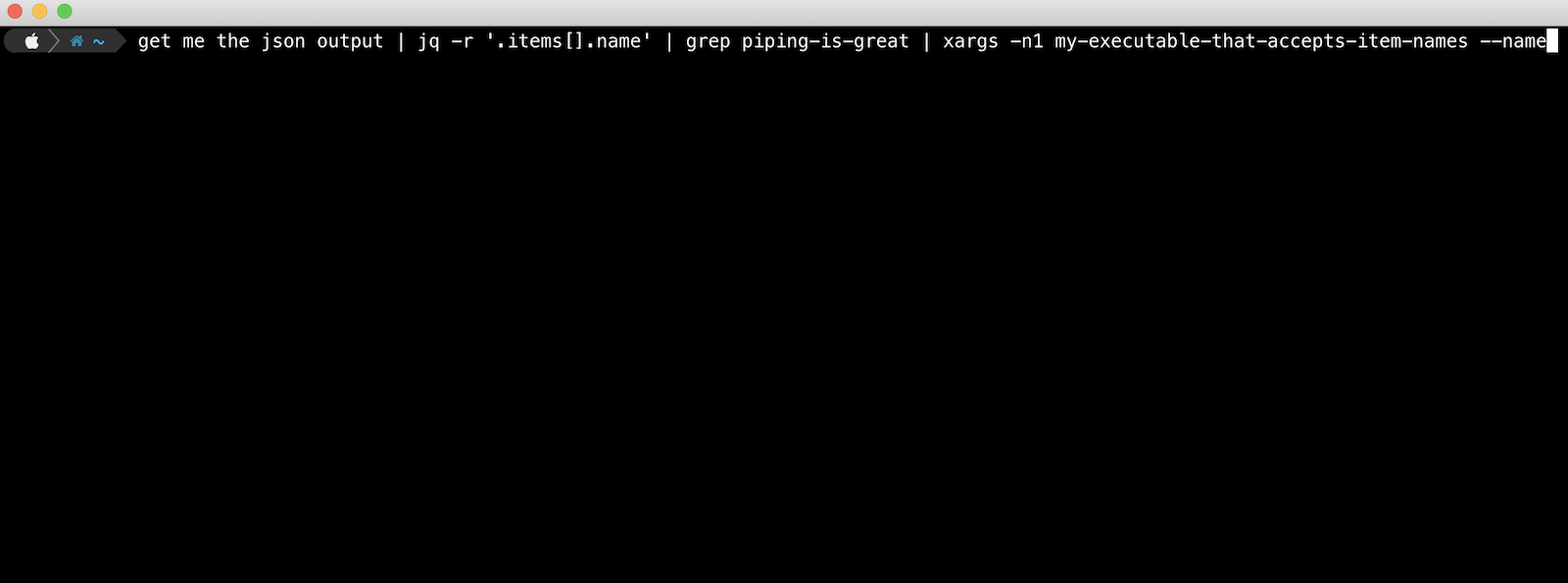
This is a quick reference post if you’re looking to pipe output into another command on Linux using xargs.
The pipeline is immensley powerful and you can leverage it to act on different stages of your full command to do specific selecting, matching, and manipulation.
Say you are running an executable that outputs a bunch of JSON and you want to select certain a certain subset of this data, pattern match it, and then send that matched data into another command.
This is the perfect use case for a mixture of the jq, grep and xargs commands in the pipeline.
Practical example with xargs
Here is a practical example where you might want to list all your AWS CodePipeline pipelines, match only on certain ones, and then execute (Release Changes) on each of them.
aws codepipeline list-pipelines | jq -r '.pipelines[].name' | grep project-xyz | xargs -n1 aws codepipeline start-pipeline-execution --name
The piped command above does the following:
- Lists all AWS CodePipelines with the command
aws codepipeline list-pipelines - Uses
jqto ‘raw’ select the name from each pipeline object in the pipelines[] array that the above command outputs - Sends each pipeline name into
grepto match only those containing the string “project-xyz” - Pipes the resulting pipeline names using
xargsinto the commandaws codepipeline start-pipeline-execution --name. The-n1argument tells xargs to use at most max-args of 1 per command line.